The GroupDocs APIs are designed to be REST compliant so that they are familiar and easy to use. This post looks at how to use Swagger to test the GroupDocs APIs. Before showing you how to run a test, it explains Swagger and REST, and why we use them.
Why we use Swagger and REST
Swagger is a specification and a framework for building interactive API documentation and sandboxes, and to generate the code of an API client. Swagger (http://swagger.wordnik.com/) was developed by http://wordnik.com in the course of the development of their own API (http://developer.wordnik.com/docs). The Swagger specification itself does not depend on specific programming languages, instead Swagger implementations are available in Scala, Java and HTML5. The API code generators (https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-codegen) are available in Scala, Java, JavaScript, Ruby, PHP, and Actionscript 3. Swagger can be found in github (https://github.com/wordnik/swagger-core) as can its supporting documentation (https://github.com/wordnik/swagger-core/wiki). To develop your own API server, you may follow the tutorial (https://github.com/wordnik/swagger-core/wiki/tutorial). You’ll find project examples there too (https://github.com/wordnik/swagger-core/tree/master/samples). The main purpose of the Swagger project is to update documentation and API clients as fast as the service itself.
Swagger UI
The Swagger UI framework allows both developers and non-developers to interact with an API server in a simple and understandable way. While visualizing all the features of API the developer can test how the server responds to parameters and variables. The Swagger UI does not have any software dependencies and is very easy to use. Built with only HTML/CSS/JavaScript, it does not have very pleasant or intuitive interface yet. It may be run both locally and on the server. It may downloaded from Github (https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui/downloads). A simple demo may be found on the Swagger developer’s website (http://petstore.swagger.wordnik.com/).
REST
REST is a style of software architecture for building distributed systems. The author of REST is Roy Fielding who is also one of the authors of the HTTP protocol. In REST, data is transferred with the help of a limited quantity of formats (HTML, XML, JSON) via HTTP. REST perfectly suits the development of extensible web-services.
Swagger UI example - GroupDocs Swagger UI
Groupdocs uses Swagger for its own purposes and seeks to help developers get familiarized with the features of our API in detaile. A Swagger UI for the GroupDocs API may be found at the following link: https://api.groupdocs.com/v2.0/spec/.. Alternatively, download your Swagger UI and acquire all the methods from this link: https://api.groupdocs.com/v2.0/spec/spec-files/resources.json. The easiest way to master an API is to follow an example. First off you need to know your API key and the client ID specific to your GroupDocs account. You can find them in GroupDocs:
- To get the API key: Select the menu option My Account, then API and API Key.
- To get the client ID: Select My Account, then API and Client ID.
Let us test an API on a simple example. Let’s say we need to acquire information on storage. Our actions:
- Open https://api.groupdocs.com/v2.0/spec/ and specify your API Key in the top right corner.
- Open the Storage tab. We see a list with all possible actions.
- Select Get storage info. [caption id=“attachment_1407” align=“alignnone” width=“802” caption=“Swagger UI home page with list of applications”]
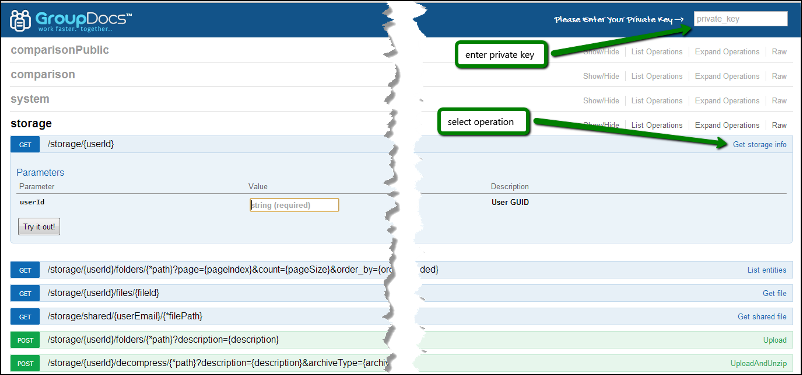 [/caption] In the frame we can see the parameters required to compile and submit a request. [caption id=“attachment_1411” align=“alignnone” width=“802” caption=“Live demo of the chosen API method”]
[/caption] In the frame we can see the parameters required to compile and submit a request. [caption id=“attachment_1411” align=“alignnone” width=“802” caption=“Live demo of the chosen API method”]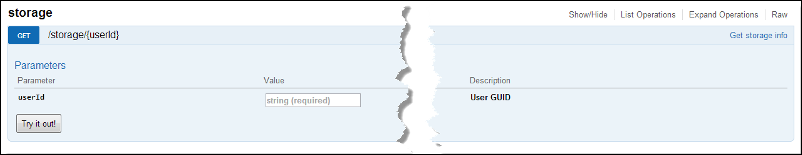 [/caption] The list of those parameters consists of three columns – parameter, value and description. The value field indicates which type of value it should be and if it is necessary or not. In our case we need to specify only one required parameter: userId, also known as Client ID, acquired above.
[/caption] The list of those parameters consists of three columns – parameter, value and description. The value field indicates which type of value it should be and if it is necessary or not. In our case we need to specify only one required parameter: userId, also known as Client ID, acquired above. - After completing all required fields, click Try it on! and wait for the server to respond. The response from the server consists of four pieces of information: Request URL, Response Code, Response Body and Response Headers. [caption id=“attachment_1418” align=“alignnone” width=“803” caption=“Swagger UI shows results of executed API method”]
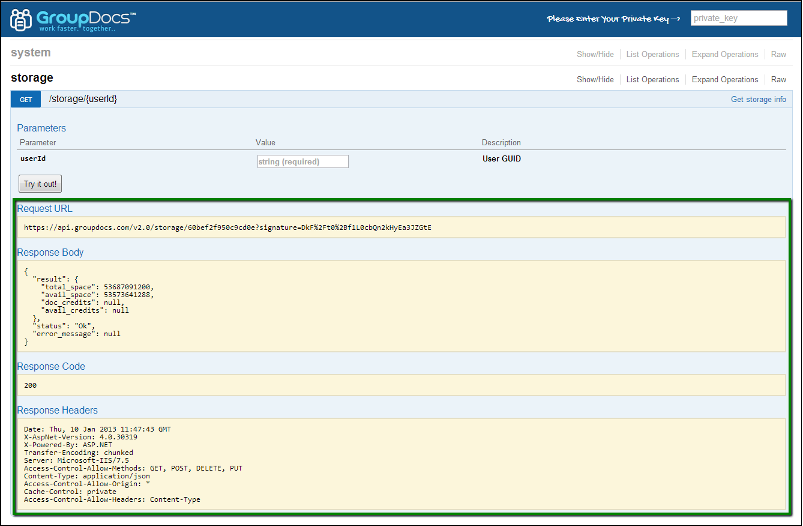 [/caption]
[/caption] - Enter the required information in the Response Body frame.
Please talk to us using our Live Chat support or official feedback forum. Stay connected with our blog and newsletter to get updates regarding all GroupDocs enhancements.